Meet the Rovers: Mars 2020
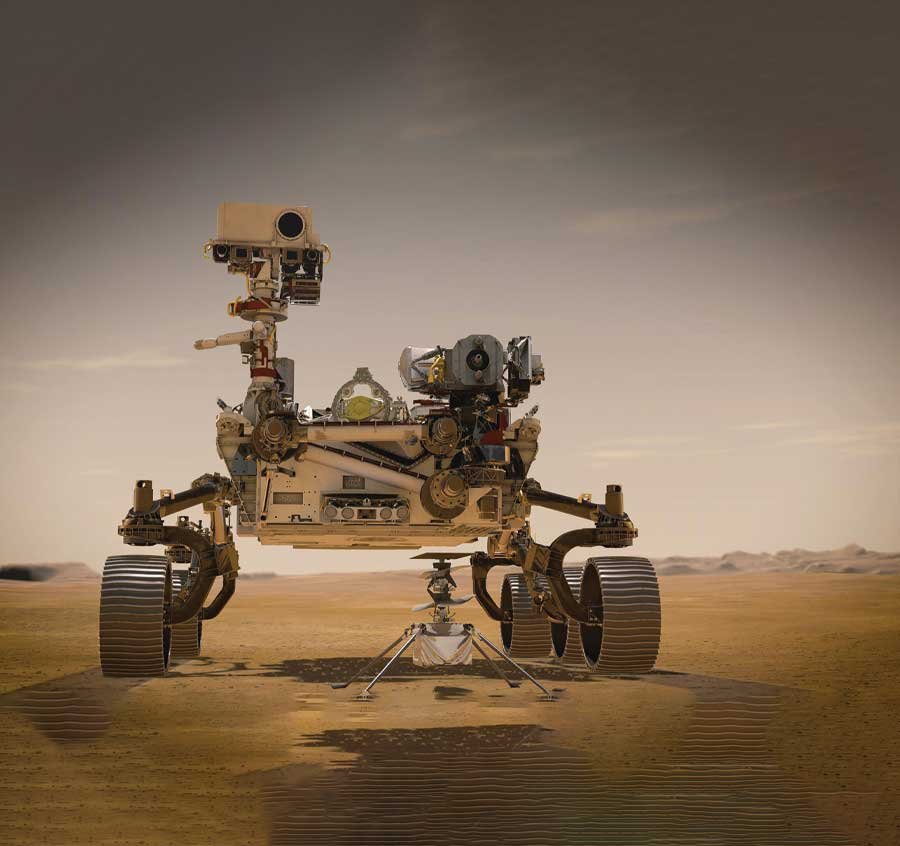

Is it possible to fly a helicopter in a thinner atmosphere? So, helicopters use the air around them to produce lift to fly. As such, can a helicopter fly on Mars? The planet’s atmosphere is only 1 percent of Earth’s atmospheric surface density. Will the helicopter still fly? Well, the answer is, yes, a helicopter can still fly. But it will be very difficult. You will need bigger and more powerful rotors to achieve flight.
Yet, how do we know this to be true? Well, on the 19th of April 2021, Ingenuity took its first flight on the surface of Mars. And accompanying Ingenuity in its first flight is The National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Perseverance. This is the story of the newest rover to arrive on Mars.
Mars 2020 Perseverance
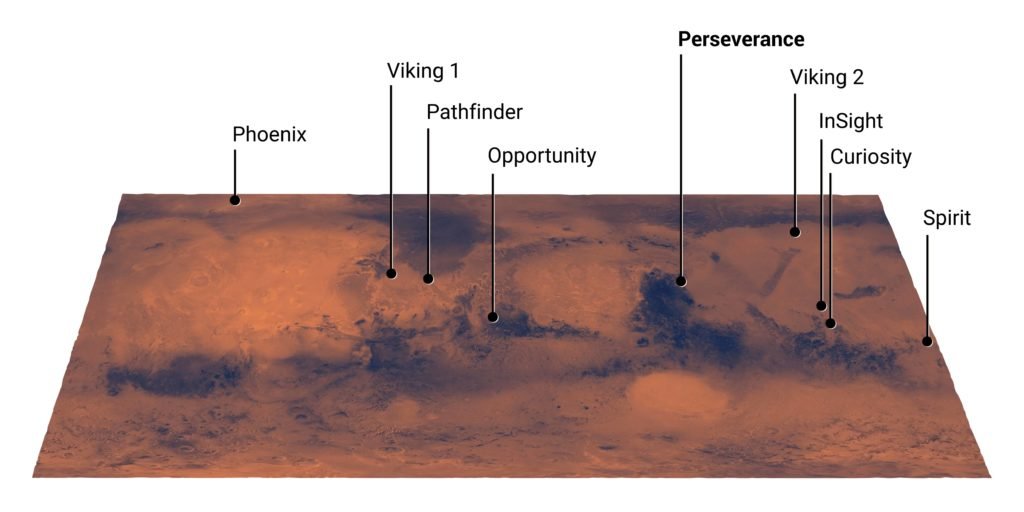
NASA created its most sophisticated rover yet, and they named it Perseverance. Its name embodies NASA’s passion, and their nation’s capability, to take on and overcome challenges. Perseverance’s mission to the red planet is similar to its siblings. Therefore, like Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, and Curiosity, it shall study the planet’s geology and climate. Perseverance’s work, like the others, will pave the way for human exploration of the planet. And its study might also find evidence of life beyond Earth.

Perseverance is even larger than Curiosity. The rover is 3 meters long, then it has a width of 2.7 meters, and a height of 2.2 meters. While its robotic arm can extend out to 2 meters in length. Because of this, the rover has an astounding 1,025 Kilograms in weight. Also, Perseverance follows in the footsteps of Curiosity. Both rovers have a six-wheel rocker-bogie design. But, Perseverance has slightly narrower and taller wheels than Curiosity. As a result, these new wheels help with improving damage tolerance and performance over Martian terrain. Thanks to these improvements, Perseverance is much more mobile than its other siblings. Now it can explore even more areas on Mars.

Moving forward, Perseverance will bring new instruments to Mars. NASA gave the rover 19 cameras and four more cameras on the spacecraft. This craft carries the rover during Entry, Descent, and Landing (ESL). In addition, footage from the rover will now have audio. Because engineers installed two microphones on Perseverance. This will make the first-ever audio recording of Mars. Here are just some of the instruments the rover brings. And in the next section, we will discuss all of Perseverance’s new instruments.
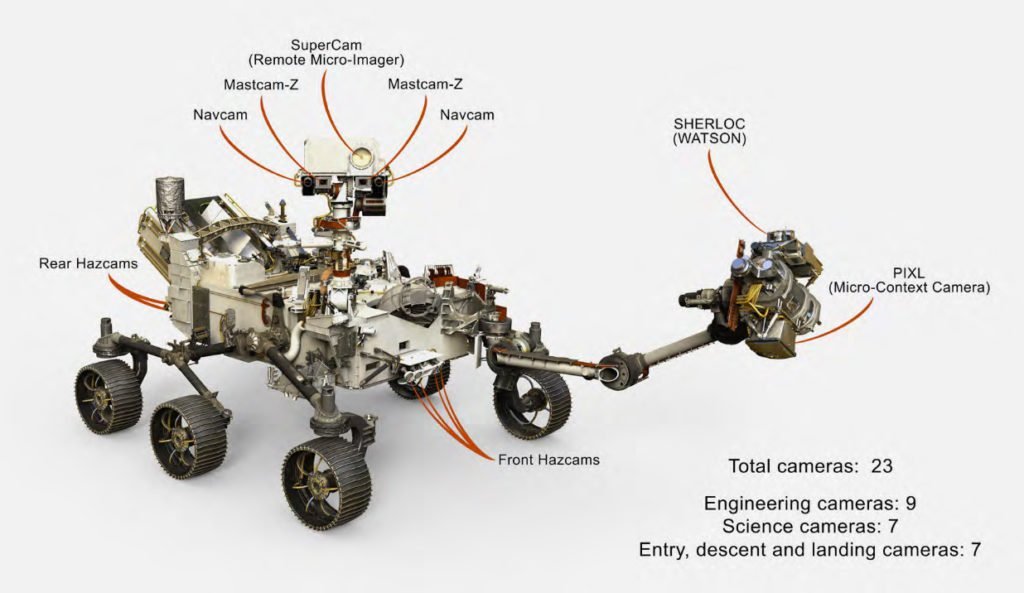
Better Instruments
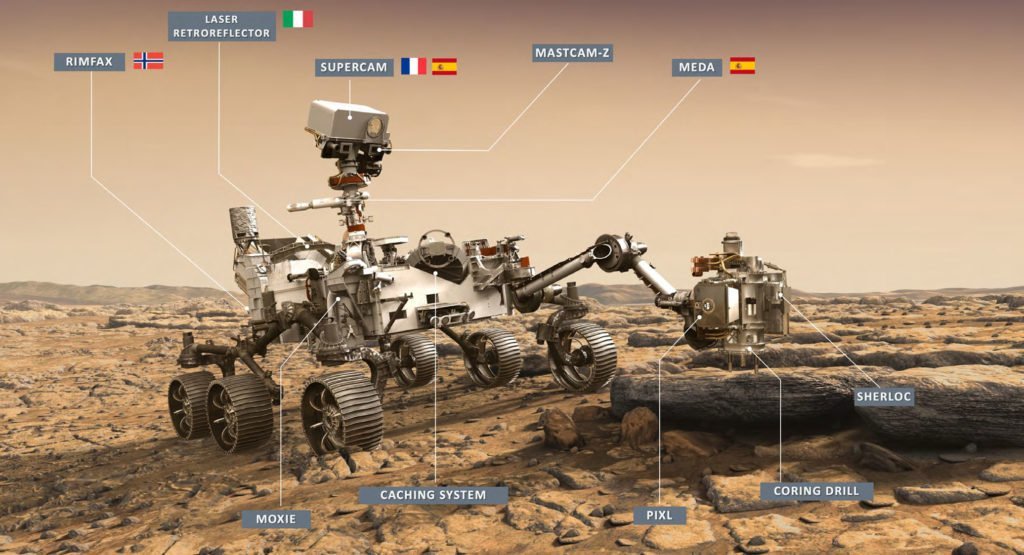

- NASA gave Perseverance new eyes called Mastcam-Z. These are a pair of next-generation science cameras on the rover’s mast or head. Compering Perseverance eye to its older siblings, Mastcam-Z is much more capable.
- Spain gave the rover MEDA (Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer). This device consists of a set of sensors placed on the rover’s mast and body. And its purpose is to study the planet’s climate and solar radiation. This will help scientists know how to build better spacesuits or habitats for astronauts.
- Continuing, this next instrument is a technology demonstrator. NASA calls this MOXIE (Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment). What it does is create oxygen from the carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere. This will be of great importance when humans finally arrive on Mars.
- On Perseverance’s arm, engineers installed a PIXL (Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry). This device uses a powerful X-ray beam at rocks. The result of beaming X-rays reveals a glow on the rock. Scientists use this instrument to study the rock’s elemental chemistry.
- Now from Norway, they give a RIMFAX (Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment) to Perseverance. Norway developed this device to use ground-penetrating radar on Mars. And for the first time, Scientists will use this to determine the different layers of the Martian surface.
- One of Perseverance’s missions is to find evidence of life. And as such, the rover has SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) on its arm. This instrument uses an ultraviolet laser to find organic compounds.
- Lastly, NASA gave the rover a SuperCam. This device is the next iteration of Curiosity’s ChemCam. Because of this, the device uses the same principle of shooting pulsed lasers to study the rocks and sediment.
Landing on Mars
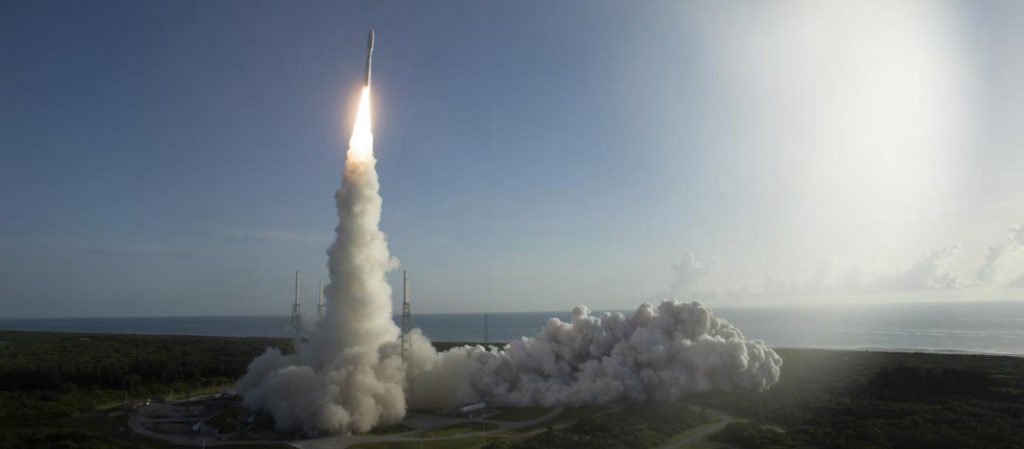

On the 30th of July 2020, NASA launched Perseverance onboard an Atlas V 541 launch vehicle. It traveled a distance of 471 million kilometers and took 203 days to reach Mars. And by the 18th of February 2021, Perseverance will perform its EDL to set foot on the Martian surface. The target landing site for Perseverance is the Jezero Crater.
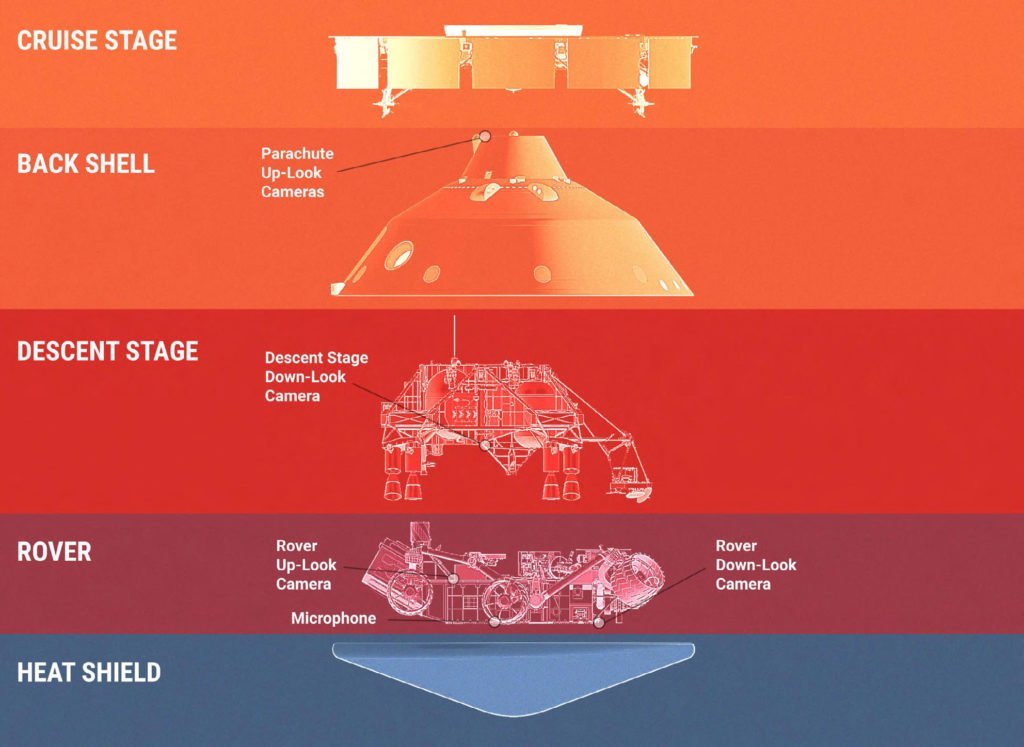
Perseverance’s EDL is akin to Curiosity. It will still use a parachute, descent rockets, and sky crane to land. But, the Mars 2020 mission will be using new navigation technology. NASA will be deploying Range Triggers and Terrain-Relative Navigation to land Perseverance.
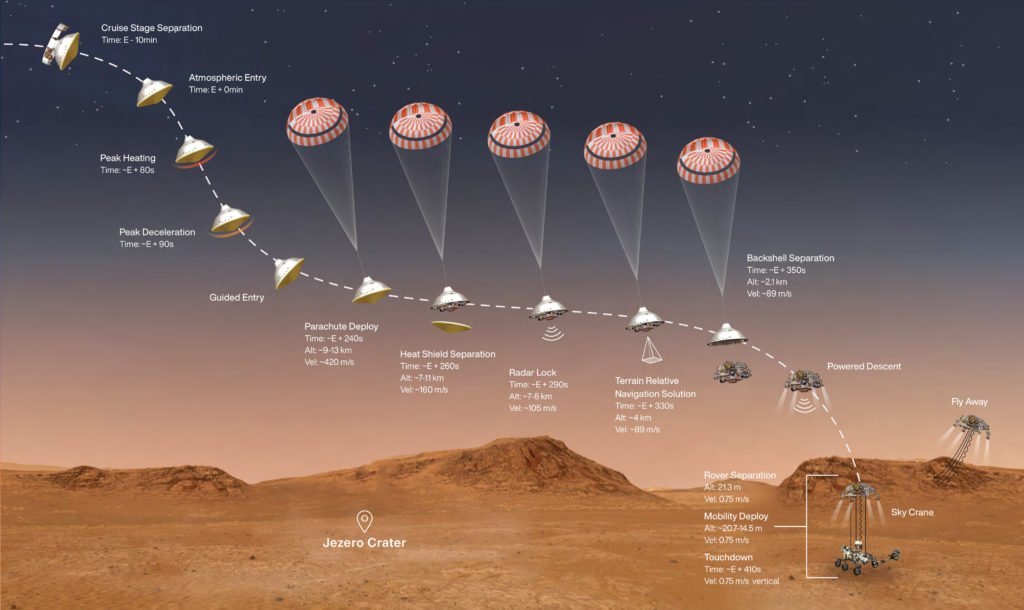
Firstly, Range Trigger is a new system that deploys the parachute based on the navigation position. This is contrary to the previous system which was based more on time and altitude. Secondly, the new terrain navigation technology is an autonomous system that pilots the spacecraft to avoid hazards. These two technologies will drastically improve the probability of success of the rover’s landing.

Results
After successfully landing on the surface of Mars. The rover switches its computer from EDL mode to surface mode. At this point, Perseverance will be conducting its studies on the Martian surface and testing its demonstration technologies. And one notable accomplishment happened on the 19th of April 2021. This day marks humanity’s first-ever helicopter flight on the Surface of Mars.
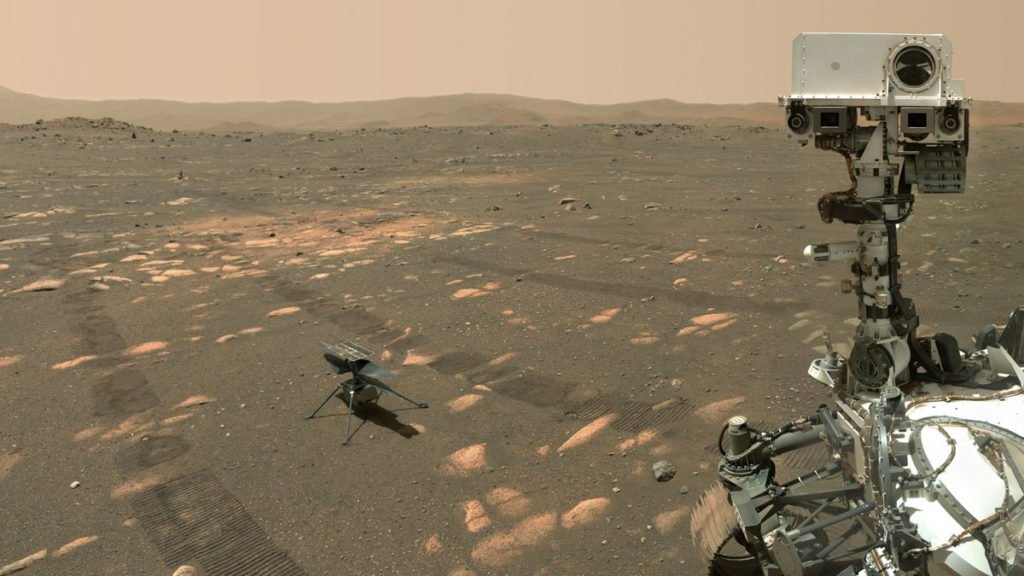

Under the belly of Perseverance lies Ingenuity. Lockheed Martin Space and NASA cooperated to develop this autonomous robot helicopter. To test this new technology, Perseverance found an open area to place the helicopter. And then given the command from Earth, Ingenuity took flight. Due to the lag in communication between Earth and Mars. Engineers built Ingenuity to be mostly autonomous. Thus, it flew under its own decision based on environmental parameters given by NASA. It was able to fly at an altitude of 3 meters and for 30 seconds it maintained a stable hover. After a total of 39.1 seconds of flight. Ingenuity landed back on the surface of Mars.
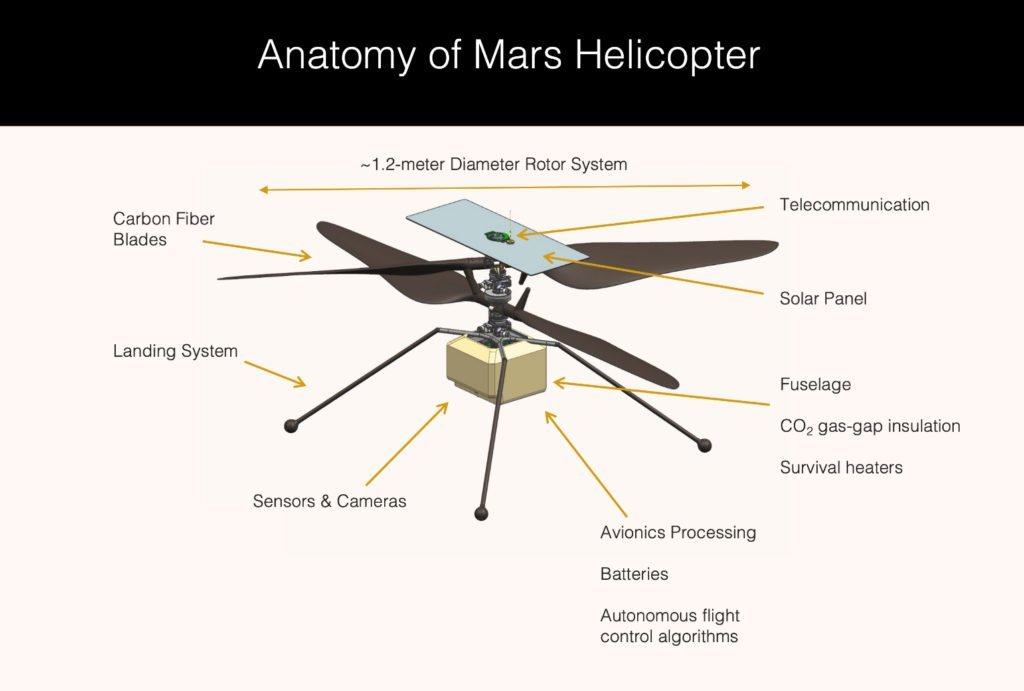
The success of Ingenuity opens new opportunities for NASA’s next missions to Mars. Future Mars helicopters could help with surveying areas too treacherous for the rovers. And by building larger helicopters, it could carry supply missions or have science instruments. This will make the study of Mars even more efficient by opening new perspectives from the air.
Humanity’s future on Mars is becoming more and more possible thanks to these ingenuities. Every day we learn more about this red planet. And lessons we learned build the foundation of evolving our species to become an interplanetary civilization. The future is bright, and let us keep it going by continuing to move forward.
Martin is your average manileño. He loves history and traveling around his beloved Metro Manila. His passion is to make the past come to life by exposing past stories not known by the general public. Tag along with him as he visits the past through the present.





