Meet the Rovers: Mars Science Laboratory (MSL)

35 years later, The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is still exploring Mars for signs of life. No, they are not trying to find an extraterrestrial. They are trying to find microscopic life or evidence of their existence. In 2011, NASA continued its pursuit to find life beyond earth. Because of this, they sent another rover to the red planet. And the name of this rover is Curiosity.
Mars Science Laboratory
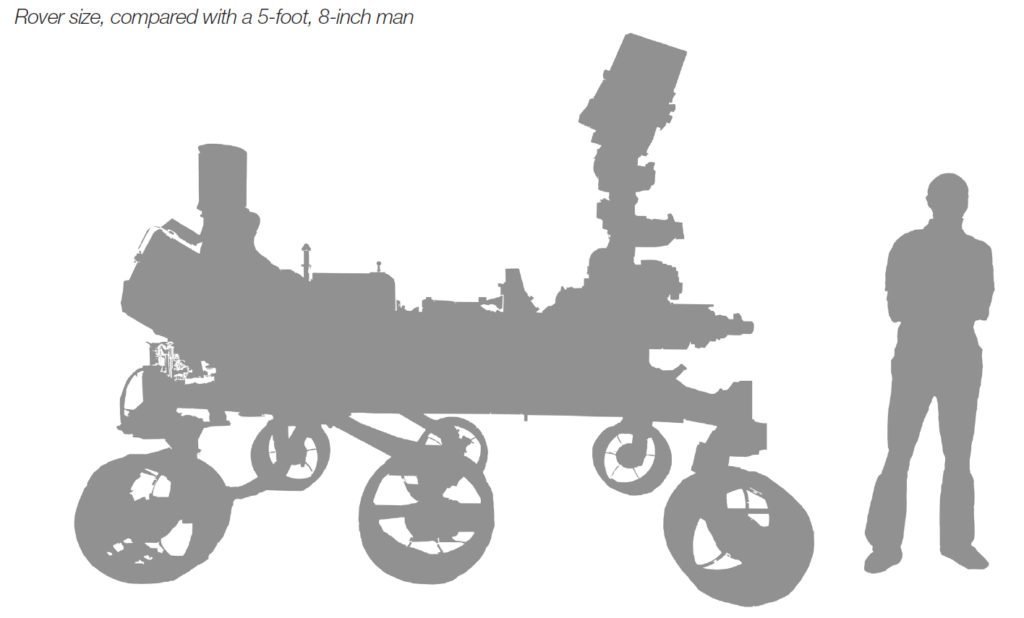
NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a surface-based mobile laboratory. This means it dwarfs Sojourner, Spirit, and Opportunity in terms of size. MSL is 3.0 meters in length and 2.8 meters in width. While the rover’s height is 2.1 meters. Overall, the rover has a mass of 899 kilograms. This makes it twice as long, five times as heavy, and has 10 times more scientific payload than MER. Furthermore, MSL is a multinational project with 400 scientists from around the world participating in the science operations.

The rover’s size and weight are reflective of the new implementations on the rover. Its mobility compared to Pathfinder and Mars Exploration Rover (MER) is a great example. It has a better suspension system called the rocker-bogie system. The rover does this by differential connecting the left and right sides of the mobility system. Because of this, all the rover’s wheels are always in contact with the ground even on rough terrain. This allows the rover to traverse the harsh landscape of Mars. And the given mobility will allow the rover to explore more of the Martian surface.
In addition, the rover has new science instruments inside. This gives NASA scientists more precise data about Mars. And possibly find evidence of life on the Planet. That is why here are some of the new instruments that NASA gave to Curiosity. This will give a better appreciation of how advanced MSL is. And explain why people call it a mobile laboratory.
More Instruments

- NASA gave Curiosity a Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam). This device uses a laser to vaporize materials to learn its chemical elements. ChemCam improves the efficiency of studying the surface by being able to analyze multiple materials on the same day.
- Curiosity also has a Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin). This uses X-rays to identify and quantify the minerals on the surface of Mars. The data retrieved from CheMin can provide a scientist with a view into Mars’ past environmental conditions.
- The rover also has a Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM). This instrument checks samples that the rover collects to find carbon-based compounds similar to Earth.
- Subsequently, it arm has a Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI). Researchers will use this handheld camera for close-up analysis of rocks and soils.
- The Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS) is a weather station inside the rover. It will assess the wind’s speed and direction. Then study Mars’s air pressure and temperature, And check the ground’s temperature and ultraviolet radiation.
- NASA installed Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) to curiosity. This is to know how radiation affects the surface of Mars. It monitors the high-energy atomic and subatomic particles coming from the sun.
- Curiosity’s Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons (DAN) will search for water underground. This device can detect hydrogen 1 meter below the surface.
- And not to forget, Curiosity also has a Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS). This device is present in both Curiosity’s progenitors, Pathfinder and MER. But the difference between them is that APXS has greater sensitivity to elements in rocks and soils
POV: Your Landing on Mars
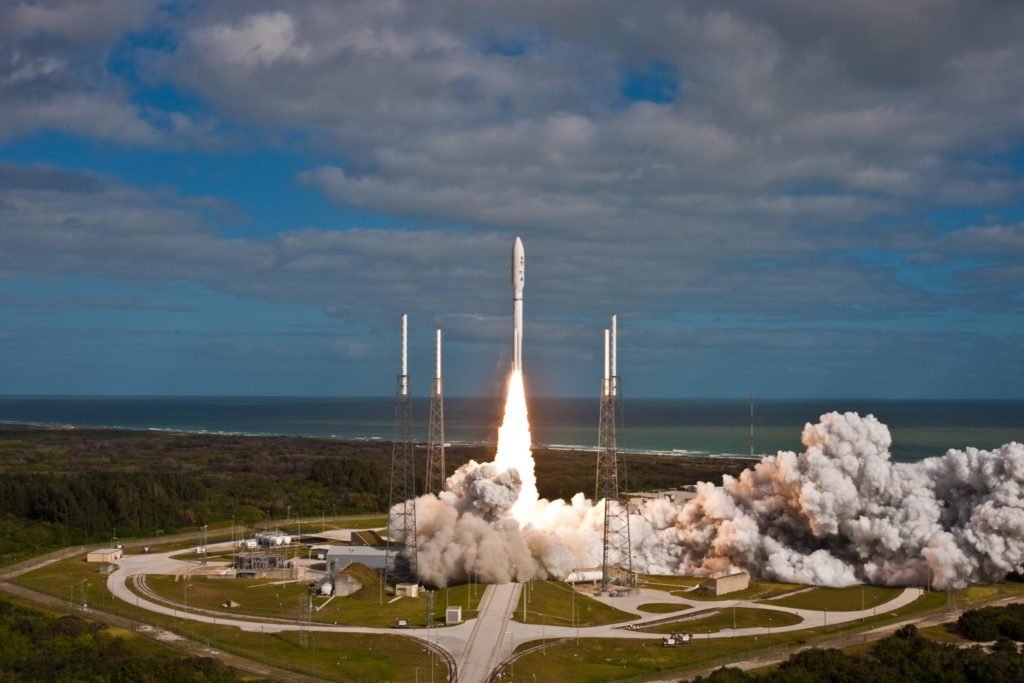

NASA launched Curiosity on the 26th of 2011, using an Atlas V 541 rocket. The rover will travel a distance of 567 million kilometers to Mars. And when it arrives, humanity will witness a new method of landing.

On the 06th of August 2012, Curiosity will be starting its Entry, Descent, and Landing (EDL) phase. The initial entry and descent of Curiosity will be similar to Viking, Pathfinder, and MER. Curiosity will still be using a parachute and rocket to decrease its descent speed. But once again, NASA has given MLS more powerful systems to make its landing more precise.
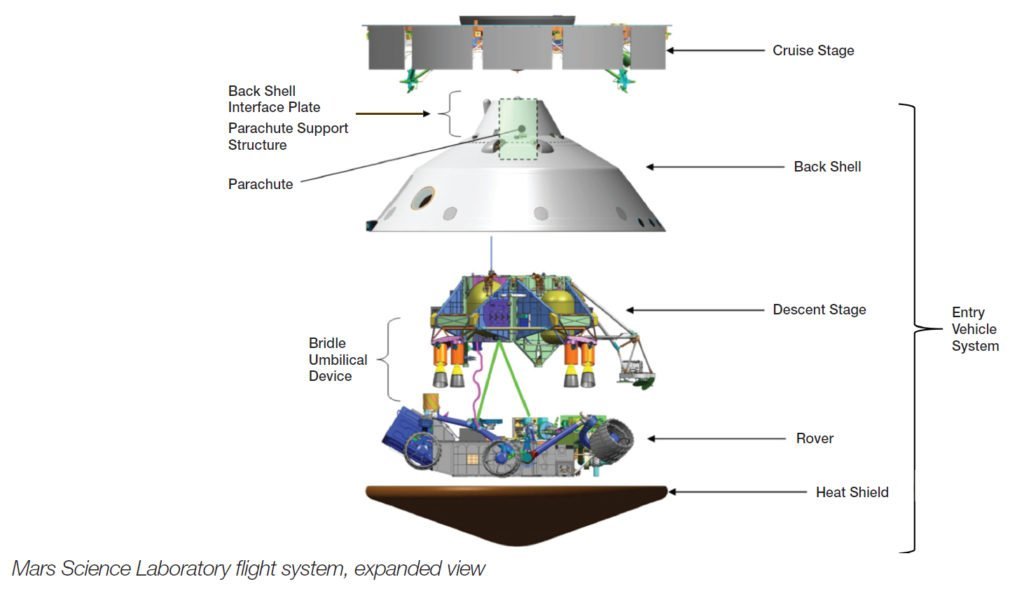
Firstly, they will be using the Mars Descent Imager (MARDI) and the MSL Entry, Descent, and Landing Instrument (MEDLI) Suite. These two systems are to collect data during EDL to know how can NASA improve its methods of landing. MARDI and MEDLI can accomplish this with their myriad of sensors to know the environmental conditions outside the rover. Then it also has cameras to navigate itself to the landing site. Additionally, this will give humanity its first footage of a rover landing. The footage will be useful for NASA’s scientists and engineers on how to improve their EDL.
Moreover, the video will give the general public its first glimpse of what a rover landing looks like. As of right now, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory has published the video on YouTube. Now anyone can view this video and see first-hand how amazing it is.
Landing with the Sky Crane

In addition to MARDI and MEDLI, Curiosity will also unveil to the world, Sky Crane. Because of Curiosity’s size, it is impractical to cocoon it inside an airbag like Pathfinder and MER. So, NASA invented a new method of landing this large machine.
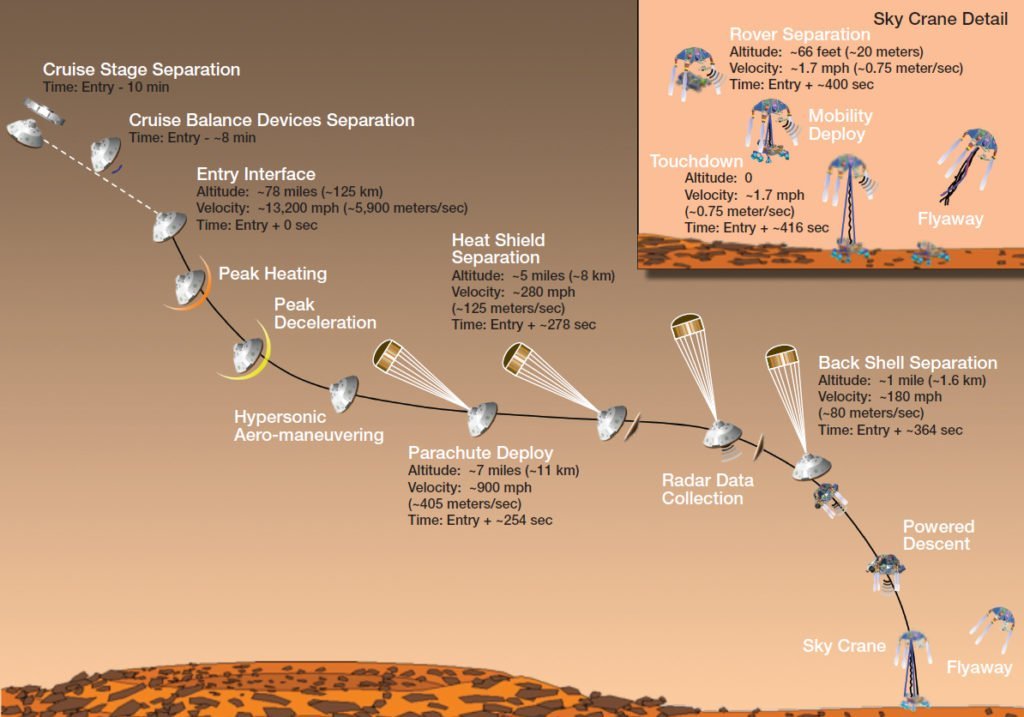
So, after the usual EDL phase of parachutes and rackets. The descent stage which carries the rover will detach from the back shell. Next, it activates more engines to reduce its descent velocity to 0.75 meters per second. Now the descent stage performs the Sky Crane maneuver. As such, the descent stage will act like a helicopter. From this point, Curiosity will descend from an altitude of 20 meters to the ground via nylon cords. Once its wheels are firmly on the ground it releases the rover from the descent stage. Then immediately after, the descent stage will launch itself to crash at a safe distance. NASA did this to ensure the stage descent does not crash onto the rover itself.
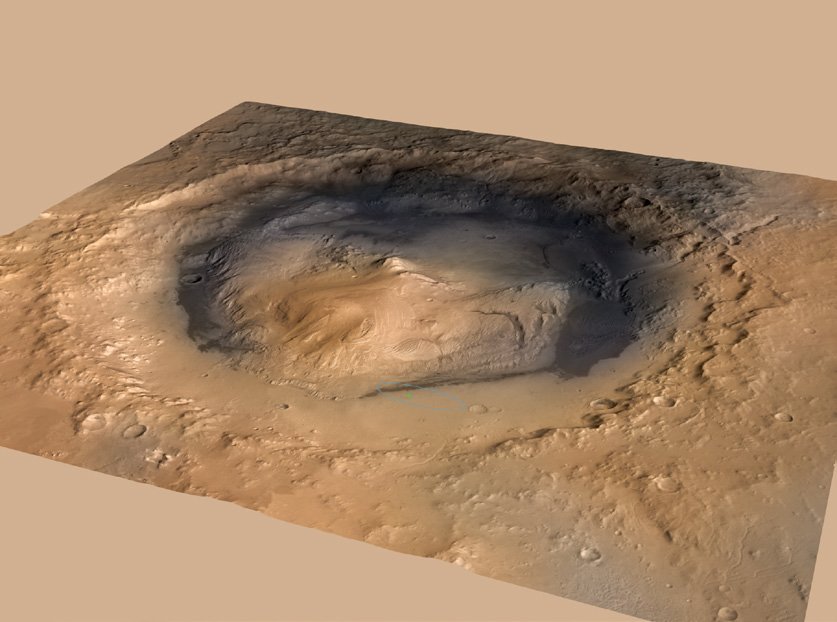
After the successful landing at Gale Crater. Curiosity will now be switching its computer to surface mode. At this time, the rover will now explore the surface. Uses all of its advanced instruments to study the planet. And as of present 2022, Curiosity is still operational. Curiosity continues to give information back to Earth for experts to study.

Results

Because of the new technologies used for Curiosity. NASA can now land heavier rovers on Mars. These rovers could have more instruments to further study the planet. Maybe in the future because of these efforts, we might find evidence of life on Mars. And might bring us to the point where we can have human exploration on Mars. But for now, NASA is planning another mission to give Curiosity some company.
Martin is your average manileño. He loves history and traveling around his beloved Metro Manila. His passion is to make the past come to life by exposing past stories not known by the general public. Tag along with him as he visits the past through the present.











