Meet the Rovers: Mars Pathfinder

When you travel it is important to do some research on your destination. This will help you figure out the essentials for your journey. As such, after research, you will know what you will need to bring and what to do for the journey. Without this information, your travel will be miserable and inefficient.
This is the same for traveling to other celestial bodies. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched a bunch of probes to the Moon before Apollo 11. If it were not for these probes collecting data, Apollo 11 would not have been a success. They brought good information on what the Apollo 11 crew would need to bring and what to do on the Moon. After Apollo, NASA set its eyes on Mars as the next destination to go. But again, before sending astronauts to the red planet they first need some research. That is why NASA has sent a bunch of orbiters, landers, and rovers to Mars.
Exploring Mars

Because of this, I would like for you to meet the rovers. NASA built these robots to study the surface of Mars. Ever since 1996, there have been five rovers on the surface of Mars. Their names are Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance. Each one of them shows the progress of technology. As each successive rover is an upgrade from one another. They improve each other’s strengths and weaknesses. And, this is a story about them.

Sadly, their stories cannot fit into one article. So, I will split these stories into four articles. And I dedicate this first article to the first rover to land on Mars, Sojourner. Then the next article will be for Spirit and Opportunity. The next article is for Curiosity and its Sky Crane. And finally, Perseverance will be the final article.
Mars Pathfinder
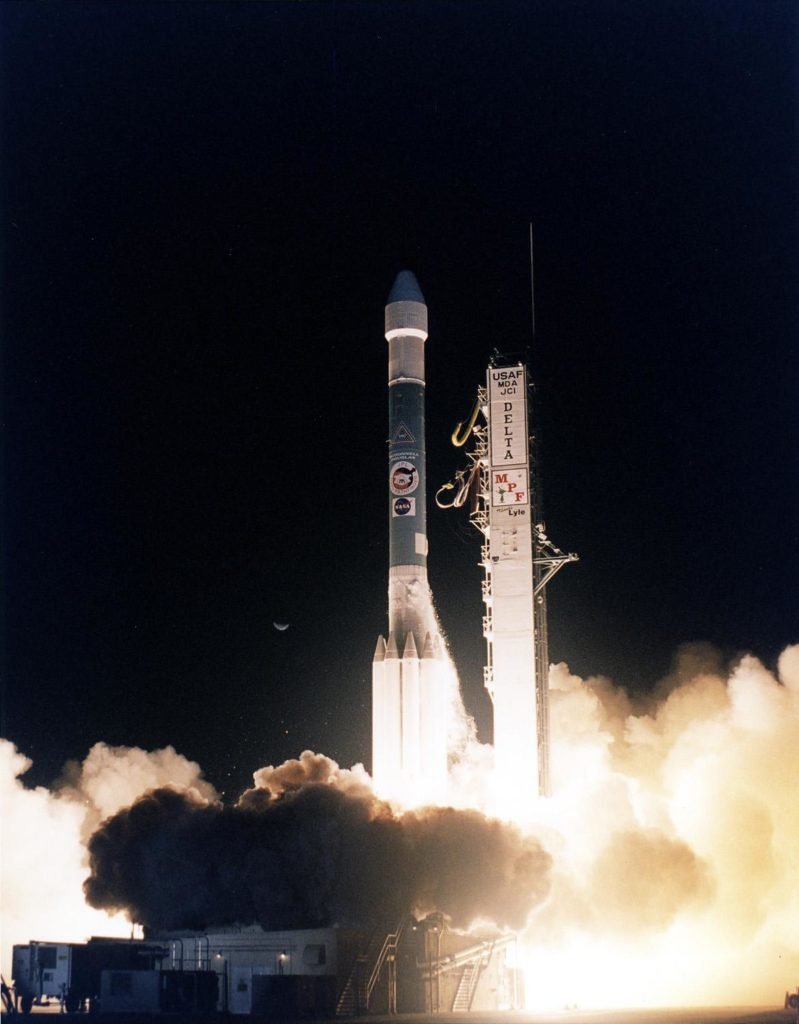

On the 4th of December 1996, NASA launched Mars Pathfinder to the surface of Mars. This is their first-ever robotic rover to be sent to Mars. The rover’s name is Sojourner. The name came from Sojourner Truth, an African-American who lived during the Civil War era. Many people know her as a champion of women’s rights and an abolitionist.

Sojourner is the first and oldest of the other rovers. As such, NASA designed the Mars Pathfinder as a technology demonstration. The first is to test the rover’s ability to move around the Martian surface. When the rover land in Mar it will be the first wheeled vehicle on another planet. Secondly, the Sojourner was to test a radically new method of landing on Mars. The rover will use the already proven method of parachutes and rockets during descent. But during landing, Sojourner will use airbags to cushion itself.
New Landing Procedure
Sojourner landed on the 4th of July 1997. The rover entered Mars’ atmosphere with a velocity of 26,460 kilometers per hour (kph). Then, Sojourner released its parachute at an altitude of 10 kilometers. Jettisoning the heat shield will take place 20 seconds later.
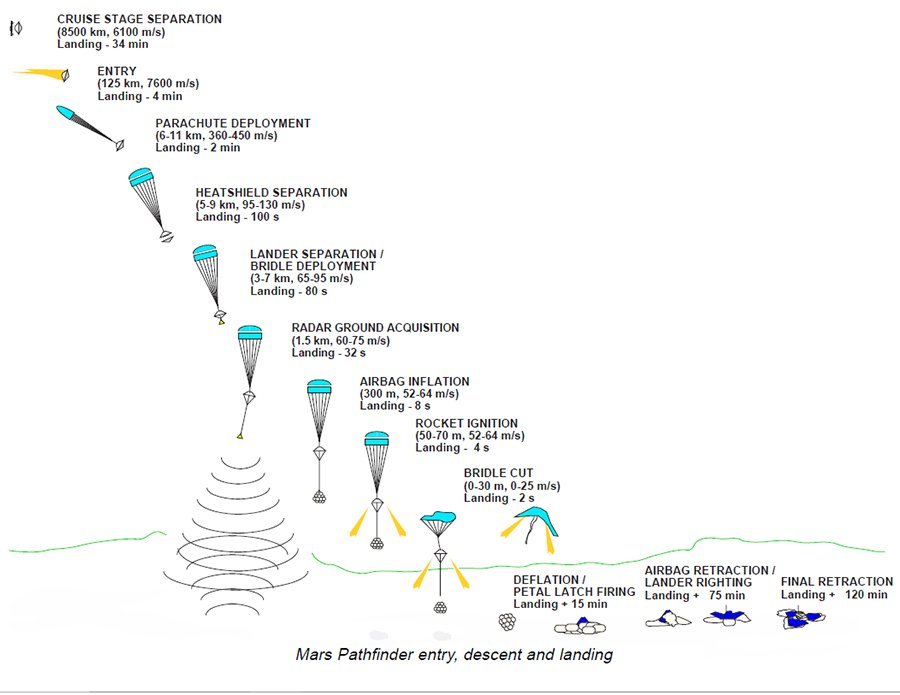
Afterward, Sojourner starts to inflate its airbags at 1.5 kilometers above the surface. And subsequently, the rocket engages to slow down its descent. These rockets last for about 2.2 seconds before landing. Separating the airbags from the parachute and backshell which contains the rockets comes next. Now Sojourner will be in free fall down to the surface. The only thing protecting the rovers are the airbags. Sojourner will bounce 15 times before completely landing Once the airbags stop moving the airbags deflate and release Sojourner.

New Instruments
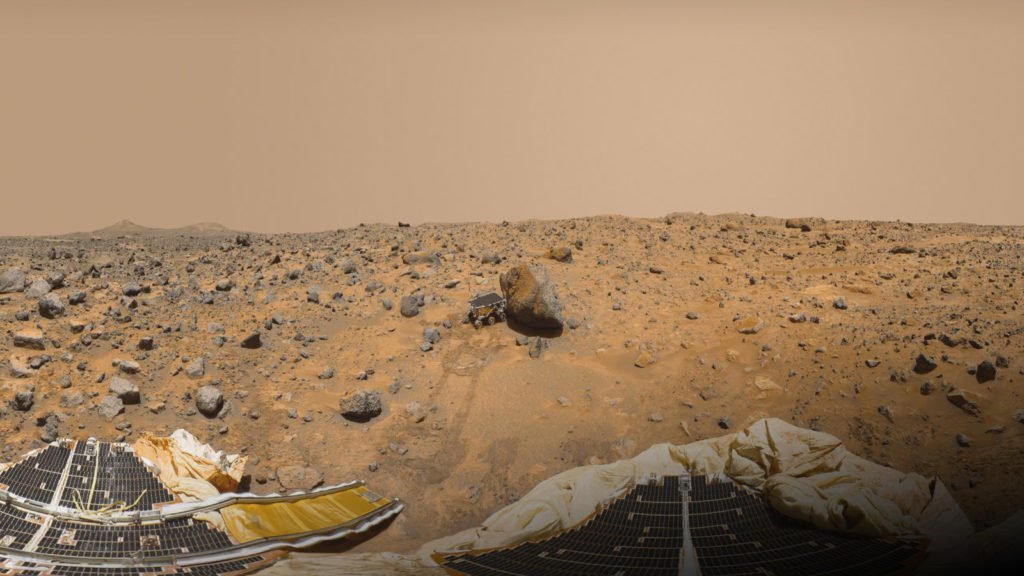
Sojourner’s landing was a success. The rover landed on a channel close to the planet’s equator called Ares Vallis. After its landing, the rover will start its prime mission. Here the rover will use its new scientific instruments.
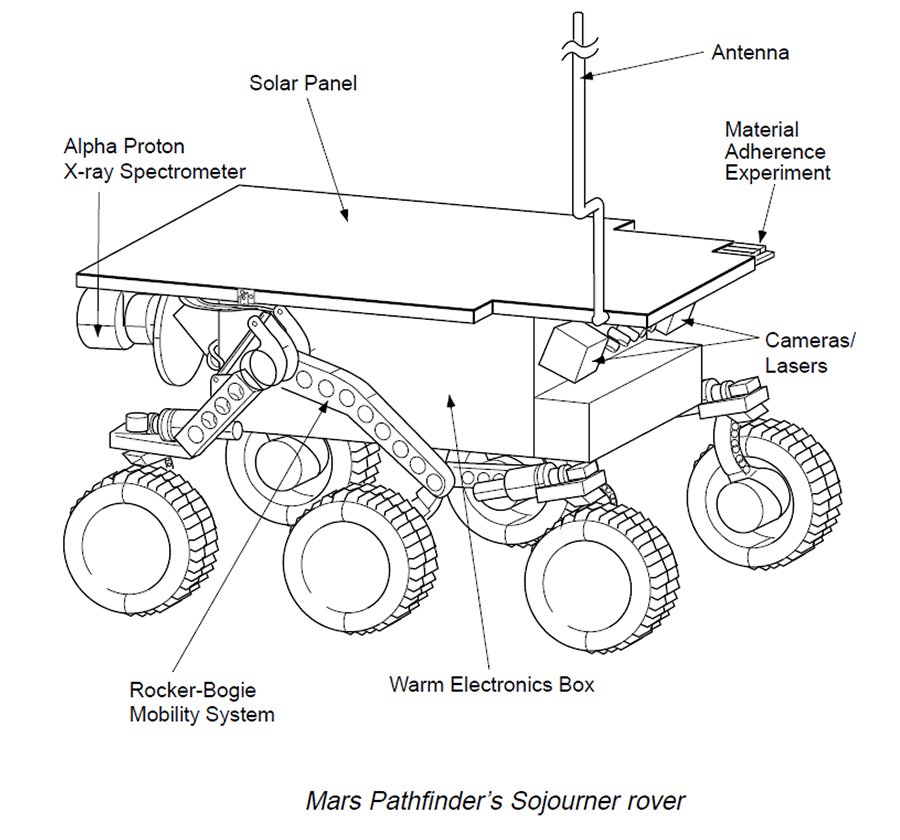
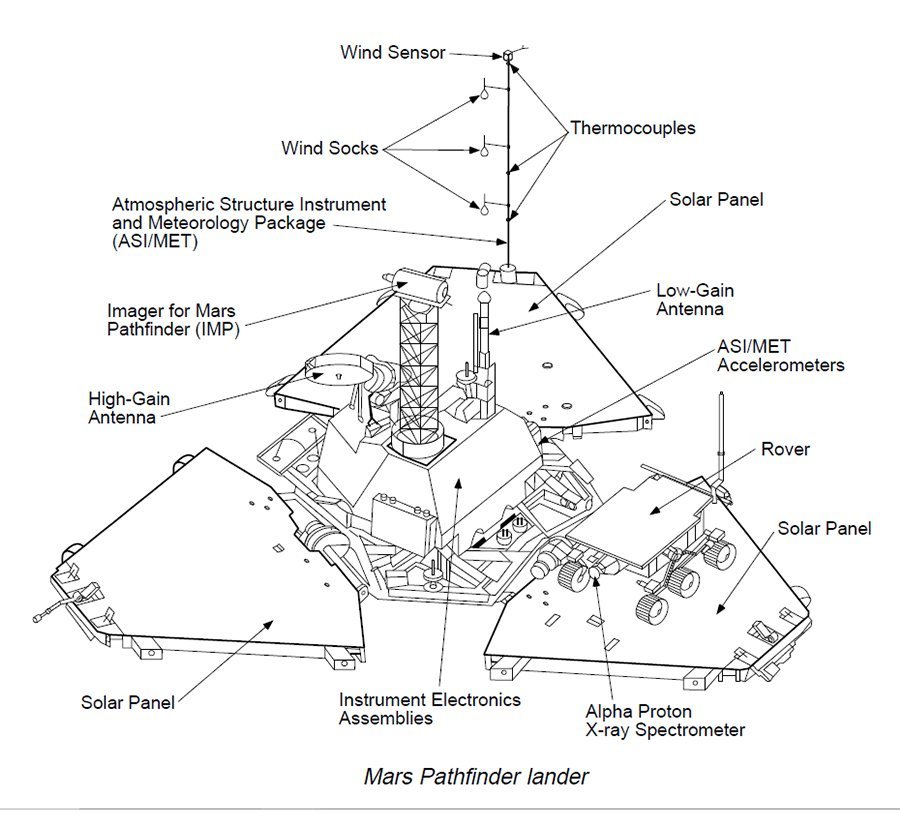
NASA gave the lander the name of Carl Sagan Memorial Station. Engineers gave the lander an Imager for Mars Pathfinder (IMP). This device consists of three cameras to capture images of the surroundings for geological studies. Furthermore, NASA gave Sojourner an Atmospheric Structure Instrument and Meteorology Package (ASI/MET). These are instruments to measure the Martian atmosphere and meteorology. And lastly, they gave the rover an Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS). This device is to study the elemental composition of rocks and soils. In combination, Sojourner can analyze the planet’s atmosphere, climate, and geology.
Results
After 83 days, Sojourner ended its mission on the 27th of September 1997. Because of this mission, we learn so much more about the red planet. Here are some things that Pathfinder has thought us. Firstly, we learned that Mars was warmer in the past. This presented to us the possibility the planet could have once liquid water on its surface. Secondly, NASA learned that ice clouds form in the lower atmosphere. This provides us with a better understanding of Mars’ past and present conditions.

The Sojourner became the pioneer of a new era of unmanned space exploration. Because the rover proves that it is possible to land heavy objects. This new possibility for more complex exploration on Mars. And surely enough more rovers are going to land on the planet.
Martin is your average manileño. He loves history and traveling around his beloved Metro Manila. His passion is to make the past come to life by exposing past stories not known by the general public. Tag along with him as he visits the past through the present.





