From Apollo to the Shuttle: New Era of Space Travel

Have you ever wondered what happened to the space program? To be more precise, what happened after the Apollo moon landing? Well, the short and simple answer is the Space Shuttle Era.
The Space Shuttle Program
By 1969, US President Richard Nixon established a space task group. This was to determine what will be NASA’s direction after the Apollo program. The result of President Nixon’s space task group was the creation of the shuttle program.

Then, by 1972, the shuttle program was announced to the public. The goal of the program was to create a reusable spacecraft. The purpose of which was to cheaply transport people and cargo to and from Earth’s orbit. The result of the program was the Space Transportation System (STS), otherwise known as Space Shuttle.
NASA made six shuttles: Enterprise, Columbia (OV-102), Challenger (OV-099), Discovery (OV-103), Endeavour (OV-105), and Atlantis (OV-104).

These are humanity’s first rocket-launch reusable spacecraft. The shuttle has the capability to land back on Earth using a regular runway. NASA also designed the shuttles to be flown 100 times before needing major refurbishment.
The Space Shuttle’s Components
There are three major components of the Space Shuttle.
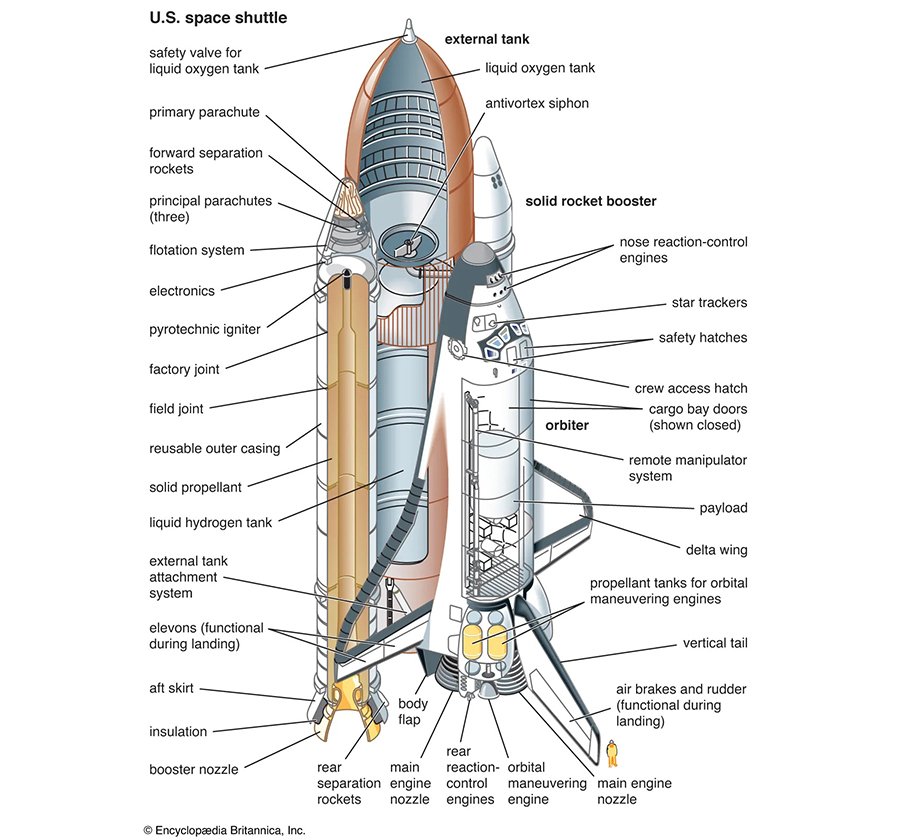
First, is the wing-shaped Orbiter. This is the spacecraft that carries both crew and cargo into orbit.
The second component is the External Tank. This component contained the fuel for the Obiter’s three main engines. You can find the External placed on the belly of the Obiter during launch.
While the third component is the Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs). These are a pair of large strap-on booster rockets to help the Orbiter get into space. You can spot the SRBs on the sides of the External Tank during take-off.
The Legacy of the Space Shuttle
The spacecraft took its maiden voyage on the 12th of April 1981. It was Columbia that made the first flight into orbit. And because of the Orbiter’s reusability, it became NASA’s workhorse.

The shuttles did a lot of things during their service. They helped with the construction of the International Space Station (ISS). NASA also used shuttles to ferry astronauts to and from the ISS. In addition, you can see NASA used shuttles to place satellites into orbit. A great example of this was the use of Discovery to place the Hubble Space Telescope into orbit. Furthermore, because of the shuttle’s cargo bay, it is able to conduct its own science experiments. They did this by putting Spacelabs inside their cargo bay.

So, if NASA wants something to be done in orbit. Then they will most definitely be using the shuttles.
Remembering Challenger and Columbia
Sadly, two catastrophic accidents caused the destruction of two shuttles.

The first accident happened on the 28th of January 1986. Challenger suffered a fatal flaw in its SRBs during take-off. This resulted in a devastating explosion that claimed the lives of seven astronauts.

17 years later another accident happened on the 1st of February 2003. During the launch of Columbia into orbit, a piece of insulating foam broke from the External Tank. This piece struck the left wing of Columbia, weakening its structural integrity. Because of this, Columbia’s left wing broke apart during its re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere. This caused the entire Columbia to explode which led to the deaths of seven astronauts.
NASA grounded all the shuttles after each accident. They did a full investigation to determine the cause of the destruction. Eventually, the space shuttles went back to service after NASA found the problems and fixed them.
End the Space Shuttle Program
U.S. President George W. Bush Jr. announced the retirement of the shuttle in 2004. Because of this, Atlantis made the last space shuttle to fly on the 21st of July 2011. This marked the end of the Space Shuttle Program.

As an appreciation of humanity’s first reusable spacecraft. NASA transferred the remaining Orbiters to museums around the US for public display. And here ends the 39-year Space Shuttle Program.
Martin is your average manileño. He loves history and traveling around his beloved Metro Manila. His passion is to make the past come to life by exposing past stories not known by the general public. Tag along with him as he visits the past through the present.






